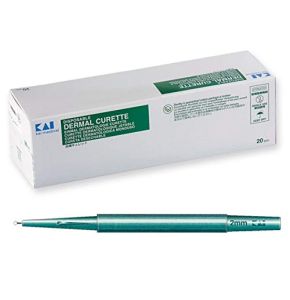
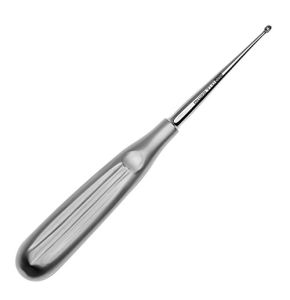
Dermatological Curette
18/11/2024 565
18/11/2024 572
18/11/2024 567
18/11/2024 412
18/11/2024 913
18/11/2024 463
18/11/2024 496
18/11/2024 561
18/11/2024 927
18/11/2024 472
18/11/2024 482
18/11/2024 548
18/11/2024 603
18/11/2024 505
18/11/2024 523
Precise and Versatile Dermatological Curettes
In this stand dedicated to the "dermatological curette," Placemed offers a collection of high-precision curettes and professional tools carefully selected for you. Designed to meet the needs of the modern dermatological expert, the dermatological curettes showcased by our partner vendors are the perfect blend of medical tradition and technological innovation. They embody the ideal tool for a wide range of dermatological interventions, offering unparalleled precision and exceptional versatility. From treating skin lesions to removing growths, our dermatological curettes ensure optimal performance with every use.
In What Cases is the Dermatological Curette the Instrument of Choice?
The dermatological curette is a key instrument in dermatology. It is used to remove skin lesions precisely. This tool is particularly effective in certain specific cases.
Among the most common indications are warts. These skin growths caused by a virus can be bothersome and unsightly. The curette allows for their removal while minimizing the risk of recurrence.
Seborrheic keratoses are another indication. These are benign lesions that often appear with age. The curette helps remove them without damaging the surrounding skin.
- Warts: effective removal of plantar and common warts.
- Seborrheic Keratoses: removal of benign age-related lesions.
- Molluscum Contagiosum: treatment of small bumps caused by a virus.
- Superficial Biopsies: tissue sampling for laboratory analyses.
By choosing the dermatological curette, professionals can effectively treat these conditions, thereby improving patient comfort.
What Are the Different Types of Dermatological Curettes and Their Applications?
There are several types of dermatological curettes, each suited to specific uses. The differences lie in the size, shape, and edge of the instrument.
Curettes vary in size, with diameters ranging from 1 mm to 7 mm. Smaller sizes are ideal for tiny lesions, while larger ones are suitable for extensive areas.
The shape of the curette can be round or oval. The round curette is versatile, while the oval shape offers increased precision for certain body areas.
- Sharp-Edged Curette: for precise tissue curettage.
- Blunt-Edged Curette: used for scraping without cutting, ideal for sensitive areas.
- Disposable Curette: offers maximum hygiene by avoiding reuse.
- Reusable Curette: made of stainless steel, it can be sterilized and reused.
The choice of curette type depends on the procedure to be performed and the practitioner's preferences.
How to Perform a Curettage Procedure Safely?
Safety is paramount during a curettage procedure. Proper technique ensures optimal results and reduces risks for the patient.
Before starting, it is important to prepare the area to be treated. The skin should be cleansed with an antiseptic to eliminate bacteria. Local anesthesia may be used for patient comfort.
Curettage Technique
The practitioner holds the curette like a pen for better control. They apply gentle pressure and make circular motions to remove the lesion. It is essential not to press too hard to avoid damaging healthy tissues.
Bleeding Control
After curettage, slight bleeding may occur. Gentle compression with sterile gauze is usually sufficient to stop it. In some cases, a hemostatic agent may be applied.
By following these steps, the procedure is carried out safely, providing the patient with effective treatment.
What Are the Hygiene and Sterilization Considerations for Dermatological Curettes?
Hygiene is a crucial aspect in dermatology. Curettes must be properly sterilized to prevent infections.
Disposable Curettes
Disposable curettes are single-use. After the procedure, they should be disposed of in a container designated for sharps. This eliminates the risk of cross-contamination.
Reusable Curettes
For reusable curettes, a sterilization protocol is necessary. After use, the instrument must be cleaned to remove residues. Then, it is sterilized in an autoclave to eliminate all microorganisms.
- Initial Cleaning: removal of debris with a soft brush.
- Disinfection: immersion in an appropriate disinfectant solution.
- Sterilization: use of the autoclave for complete sterilization.
- Storage: keeping in sterile packaging until next use.
By adhering to these measures, professionals ensure the safety of patients and staff.
What Are the Post-Procedure Care Recommendations After Using a Dermatological Curette?
After a curettage procedure, the patient should follow certain recommendations for proper healing.
It is important to keep the area clean and protected. A dressing may be applied to prevent infection. The patient should change the dressing regularly according to the doctor's instructions.
Home Care
The patient should clean the area with a saline solution or a mild soap. It is advisable to avoid using harsh products that can irritate the skin.
Signs to Watch For
If the patient notices signs of infection, such as excessive redness, swelling, or pus, they should consult a doctor immediately.
- Avoid Sun Exposure: protect the area from UV rays to prevent scarring.
- Do Not Scratch: avoid touching or scratching the area to promote healing.
- Follow Instructions: adhere to the doctor's advice for local care.
By following these recommendations, the patient contributes to rapid healing and reduces the risk of complications.
In conclusion, the dermatological curette is an indispensable instrument in dermatology. It allows for the effective treatment of various skin conditions. Choosing the right type of curette, mastering the technique, and adhering to hygiene protocols are essential to ensure patient safety and comfort. Post-procedure care also plays a key role in the success of the treatment. Healthcare professionals must pay attention to each step to provide the best possible care to patients.
 Francais
Francais