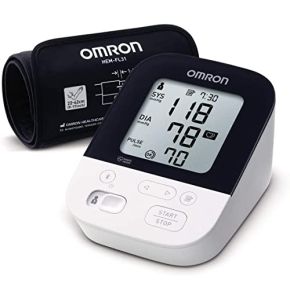
Blood pressure monitor
3700446008871 18/11/2024 298
3700446008888 18/11/2024 283
3700446008611 18/11/2024 417
3700446002077 18/11/2024 338
3700446008628 18/11/2024 272
3700446007232 18/11/2024 338
3700446007195 18/11/2024 467
3700446008413 18/11/2024 375
Spengler Lian Classic Children's Sphygmomanometer - Double Tubing, Patterned Cotton Velcro Cuff
3700446008727 18/11/2024 392
3700446024741 18/11/2024 282
18/11/2024 260
18/11/2024 288
18/11/2024 233
18/11/2024 266
18/11/2024 307
18/11/2024 323
18/11/2024 286
18/11/2024 264
18/11/2024 260
18/11/2024 259
A Professional Blood Pressure Monitor for Accurate Measurement!
Measuring blood pressure is essential for preventing and diagnosing hypertension and cardiovascular diseases. Blood pressure monitors are indispensable tools for healthcare professionals. On Placemed, we offer a wide range of professional medical instruments tailored to your needs, whether you're a doctor, nurse, or other healthcare provider.
Introduction to Blood Pressure Measurement
Blood pressure indicates the force of blood circulating in the arteries. Accurate measurement is crucial to detect hypertension, a condition affecting many people and potentially leading to serious heart problems. Healthcare professionals use blood pressure monitors to measure and monitor their patients' cardiovascular health.
History and Evolution of Blood Pressure Monitors
The first blood pressure measurement devices were mercury sphygmomanometers. These instruments were accurate but bulky. Over time, they evolved into aneroid and electronic models. Today, we have electronic models, lightweight manual devices, and even connected monitors. These innovations have improved medical diagnosis and simplified blood pressure measurement.
Types of Blood Pressure Monitors
There are several types of blood pressure measurement devices suited to different uses:
- Manual Monitors: Manual models, such as arm blood pressure monitors, are often used in clinical settings. They require training for proper use but offer precise readings. This option is ideal for professionals who prefer the traditional method.
- Electronic Monitors: These devices can be automatic or semi-automatic. Arm electronic blood pressure monitors are easy to use and provide quick readings. Simply place the cuff and press a button to get results.
- Wrist Monitors: These are convenient for home use. Compact and portable, they may be less accurate than arm monitors.
- Connected Monitors: Modern devices allow blood pressure tracking via a mobile app. They are useful for remote monitoring and engaging patients in their health management.
How to Choose the Right Blood Pressure Monitor
To select the appropriate device, consider the following criteria:
- Accuracy and Reliability: Ensure the measurement device is clinically validated. Accurate readings are essential for reliable medical diagnosis.
- Type of Device: Choose between manual, electronic, or connected monitors based on your needs and practice.
- Cuff Size: Ensure the cuff fits the patient's arm to avoid inaccurate readings. Some models offer interchangeable cuffs.
- Additional Features: Options like arrhythmia detection, memory for previous readings, or connectivity can be beneficial.
Best Practices for Using a Blood Pressure Monitor
To obtain accurate blood pressure readings, follow these practices:
- Patient Positioning: The patient should be seated, relaxed, with their arm at heart level. It's recommended to wait a few minutes before taking a reading.
- Cuff Placement: The arm cuff should be placed on bare skin without tight clothing. For wrist monitors, ensure the wrist is at heart level.
- Measurement Conditions: Avoid taking readings after physical activity, caffeine, or tobacco use, as these can skew results.
Maintenance and Care for Blood Pressure Monitors
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure reliability:
- Regular Calibration: Periodically calibrate your device to maintain accuracy. Check the manufacturer's recommendations.
- Cleaning and Disinfection: Clean the cuff and device after each use, especially in clinical settings, to prevent cross-contamination.
- Proper Storage: Store your device in a dry place, away from humidity and extreme temperatures.
Recent Innovations and Future Trends
Blood pressure monitors have significantly evolved in recent years:
- Connected Models: They enable blood pressure tracking through mobile apps, facilitating remote monitoring and telemedicine.
- Advanced Technologies: Some models detect arrhythmias or calculate systolic and diastolic pressure with high precision.
- Patient Engagement: Modern devices encourage patients to regularly monitor their blood pressure, improving hypertension management.
Regulatory and Compliance Aspects of Blood Pressure Monitors
These instruments are medical devices subject to strict standards:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure the device complies with current regulations and holds the necessary certifications.
- Clinical Validation: A professional medical blood pressure monitor must be clinically validated for accurate readings.
Why Choose Your Device on Placemed
Placemed offers a wide range of instruments tailored to your needs:
- Quality and Reliability: Our devices are precise, reliable, and meet medical standards.
- Wide Selection: Whether you need an arm monitor, wrist monitor, or electronic monitor, you'll find the right device.
- Advanced Features: Explore monitors with features like arrhythmia detection or mobile connectivity.
- Professional Advice: Our team is here to help you choose the best device for your practice.
By choosing a blood pressure monitor on Placemed, you're opting for a high-quality device that will help you care for your patients. Browse our selection and contact us with any questions.
 Francais
Francais