Spirometer
Spirolab Portable Tabletop Spirometer with Oximetry Function, 7-Inch Touchscreen, and Integrated Thermal Printer
Price on request18/11/2024 377
Spirodoc Duo – Portable Multifunctional Spirometer with Touchscreen and 3D Oximetry Function
Price on request07/04/2025 406
MiniSpir USB Spirometer for Computer – Compact Technology, Lightweight, and Easy to Carry
Price on request08/04/2025 437
18/11/2024 292
18/11/2024 334
18/11/2024 293
18/11/2024 272
18/11/2024 234
18/11/2024 248
Spirometer: An Essential Tool for Measuring Respiratory Capacity!
At this booth, Placemed offers you a comprehensive range of devices for measuring breathing, specially designed for healthcare professionals. We have chosen the best brands to meet all your needs. You will find portable spirometers, convenient for home consultations, as well as fixed models suitable for medical practices. These spirometry devices are indispensable in pulmonology for detecting and monitoring respiratory diseases.
What Is Spirometry?
Spirometry is a medical test that evaluates how well the lungs function. It measures how much air a person can inhale or exhale, as well as the speed at which the air flows. In pulmonology, this exam is very important for detecting respiratory diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or pulmonary fibrosis.
Accurate diagnosis and regular follow-up make it possible to better treat these lung diseases. Thanks to spirometry, doctors obtain precise information about the patient's respiratory status. They can then adjust treatments and monitor how the diseases progress. Without this examination, it would be difficult to know whether a treatment is effective or if breathing problems are worsening.
How Does Spirometry Work?
Spirometry measures several key parameters of lung function. The main parameters are FEV1 (Forced Expiratory Volume in One Second), FVC (Forced Vital Capacity), and the FEV1/FVC ratio.
- FEV1: This is the volume of air that the patient can exhale in one second after a maximum inhalation. It is crucial for assessing airway obstruction.
- FVC: This is the total amount of air that the patient can exhale after a maximum inhalation. It helps assess total lung capacity.
- FEV1/FVC Ratio: This ratio helps determine the type of respiratory disease. A low ratio indicates airway obstruction.
The results are shown as flow-volume curves, which represent airflow according to the exhaled volume. These curves allow for a visual interpretation of lung function and help identify any breathing abnormalities.
What Are the Clinical Applications of a Spirometer?
Diagnosis of Asthma, COPD, and Pulmonary Fibrosis
The spirometer is an essential medical device for diagnosing common respiratory diseases. In cases of asthma, it can detect a reversible airway obstruction. For COPD, spirometry shows a persistent obstruction that does not fully improve with bronchodilators. Pulmonary fibrosis, on the other hand, manifests as a reduction in total lung capacity.
Early diagnosis helps initiate appropriate treatment. This improves patients' quality of life and reduces the risk of serious complications.
Assessment of Disease Severity and Control
Spirometry helps measure the severity of respiratory diseases and track their progression over time. By regularly evaluating spirometric parameters, physicians can adjust treatments according to the patient's needs. This is especially important for chronic diseases like COPD, where disease control is essential to prevent deterioration of lung function.
By monitoring changes in spirometric parameters, healthcare professionals can identify early exacerbations and intervene quickly, thereby avoiding potential complications.
What Are the Different Types of Spirometers?
There are several types of spirometers depending on the intended medical use. Each model meets a specific need of healthcare professionals.
Portable Spirometer
These small devices make it easy to conduct respiratory tests outside of a medical office. They are practical for home visits, outpatient care, or in areas with limited healthcare access. They offer quick management of lung diseases.
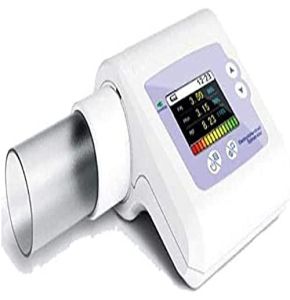
Fixed Spirometer for Medical Practices
These models are installed directly in medical offices. They offer high accuracy and enable an in-depth analysis of respiratory function. They are particularly suitable for regular follow-up of patients suffering from chronic respiratory diseases such as asthma or COPD.
Electronic Connected Spirometer
This type of device includes digital technology. It can automatically transfer respiratory data to a computer or electronic medical record. Results can then be analyzed immediately, making it easier to track the patient's breathing capacity.
Turbine or Ultrasound Spirometer
Turbine spirometers use a rotating blade driven by the patient's breath to measure the exhaled airflow. Ultrasound models use sound waves to accurately measure airflow, without any mechanical parts. The latter type has the advantage of being particularly reliable and easy to maintain.
Choosing the right type of spirometer therefore depends on the location of use, the frequency of tests, and the specific medical needs of the patients.
What Are the Best Practices for Using a Spirometer?
Preparing the Patient
Proper patient preparation is essential for obtaining accurate spirometric results. Here are a few key steps:
- Explain the test: Inform the patient about how the test will proceed to put them at ease and improve their cooperation.
- Correct positioning: Make sure the patient is sitting comfortably, upright, with the nose clipped to avoid air leaks.
- Clear instructions: Ask the patient to take a deep breath and exhale as forcefully and as long as possible.
These steps ensure that the patient performs the necessary breathing efforts correctly for accurate measurements.
Correct Technique for Reliable Results
Proper technique in performing spirometry is crucial for obtaining reliable results. Here are a few best practices:
- Ensure a good seal around the mouthpiece: The patient must maintain a tight seal between the lips and the device's mouthpiece to avoid air leaks.
- Encourage a strong exhalation: Encourage the patient to exhale as forcefully and for as long as possible into the mouthpiece for accurate measurements.
- Repeat the test: Perform several attempts to ensure consistency.
Correct technique minimizes errors and improves the reliability of spirometric results.
How to Maintain Your Spirometer?
Regular maintenance of your spirometer is essential to ensure its longevity and accuracy. Here are a few maintenance tips:
- Cleaning: Wipe the device with a soft cloth after each use to remove dust and residues.
- Checking parts: Regularly inspect the hoses, sensors, and other components for any wear or damage.
- Calibration: Perform periodic calibration according to the manufacturer's recommendations to ensure accurate measurements.
- Proper storage: Keep the device in a dry place, protected from dust and shocks when not in use.
By following these best practices, you ensure that your spirometer functions correctly and extend its service life.
 Francais
Francais